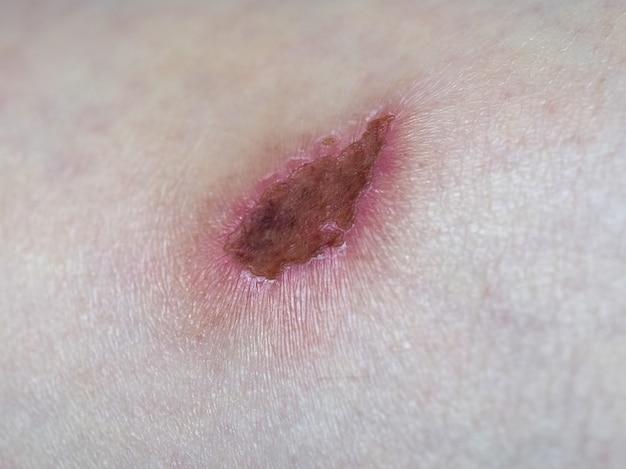
Blood draws are a common medical procedure that many of us have experienced at some point in our lives. Whether it’s for routine testing, donating blood, or receiving medication, blood draws are a necessary and important part of healthcare. But have you ever wondered if there can be any long-term effects from these procedures?
In this blog post, we will explore the question, “Can you get scar tissue from blood draws?” We’ll delve into the possible complications, such as lumps, swelling, nerve damage, and even the formation of scar tissue. Join us as we uncover the answers to these frequently asked questions and provide insights into the recovery process. If you’ve ever been curious about what happens to your body after a blood draw, then keep reading to discover the truth.
So let’s get started and clear up any doubts about the potential risks and outcomes associated with blood draws. By the end of this blog post, you’ll be well-informed about the likelihood of scar tissue formation from blood draws, as well as the various concerns that patients may have. Stick around to learn more about the recovery time, complications, and how your body heals from these seemingly routine procedures.
Can You Get Scar Tissue From Blood Draws
When it comes to blood draws, most of us have had our fair share of experiences. Whether it’s for routine check-ups or diagnostic tests, those little vials of blood can sometimes make us squirm or feel like a pincushion. But with all the poking and prodding, can you really end up with scar tissue? Let’s dive into this prickly topic and separate fact from fiction.
Understanding Scar Tissue
To answer the burning question, we first need to understand what scar tissue is. Scar tissue forms as part of the body’s natural healing process when there is an injury or trauma to the skin or underlying tissue. It’s made up of collagen fibers, which function to repair and strengthen the damaged area.
The Needle and the Damage NOT Done
Fortunately, for all you blood work veterans out there, the good news is that blood draws generally do not result in scar tissue formation. These procedures involve a quick needle puncture through the skin and into a vein. While you may experience some temporary soreness or bruising, the tiny puncture wound typically heals without leaving a lasting mark.
Exceptions to the Rule
Now, before you breathe a sigh of relief, there are a few exceptions to keep in mind. In rare cases, individuals may have a condition called hypertrophic scarring, where excess scar tissue forms. This can occur as a result of an overactive healing response or genetic predisposition. If you fall into this category, it’s essential to communicate your concerns with your healthcare provider before any blood draw.
Tips to Minimize Discomfort
Although scar tissue isn’t a significant concern when it comes to blood draws, let’s shift our focus to a more lighthearted topic – how to make the experience less torturous. Here are a few tips to minimize discomfort during your next encounter with a needle-wielding healthcare professional:
Deep Breaths and Distractions
Take a deep breath and try to distract yourself. Some people find that engaging in conversation or watching a captivating video can help ease their anxiety and take their mind off the needle.
Don’t Be a Looky-Loo
If you’re squeamish, it’s probably best to avoid glimpsing at the needle. Ignorance is bliss, right? Just close your eyes, listen to the sweet sound of a well-curated playlist, and let the healthcare professional do their thing.
Ice, Ice Baby
Before the blood draw, consider applying a cold compress or ice pack to the area. This can help desensitize the skin and reduce any potential pain or discomfort during the procedure.
Hooray for H2O
Staying hydrated is always important, but it can be especially helpful before a blood draw. Drinking plenty of water can plump up your veins, making them more accessible and easier to locate.
So there you have it – scar tissue from blood draws isn’t a common occurrence. Unless you’re one of the lucky few with a predisposition to hypertrophic scarring, you can breathe a sigh of relief knowing that those routine blood tests won’t leave you with lasting battle scars. Remember, though, it’s essential to communicate any concerns with your healthcare provider to ensure a comfortable and stress-free experience. And if all else fails, ice cream afterward always helps!
FAQ: Can You Get Scar Tissue From Blood Draws
Why is there a lump where I got blood drawn
When you get blood drawn, it’s not uncommon to notice a small lump at the site where the needle was inserted. This lump is typically a hematoma, which is a collection of blood that has leaked from the punctured blood vessel. It usually resolves on its own within a few days or weeks, but if you’re concerned or it becomes painful, it’s best to consult with your healthcare provider.
Why is my arm swollen after getting blood drawn
Swelling in the arm after a blood draw is often a result of the body’s natural response to tissue injury. When a needle pierces a blood vessel, it can cause some bruising and inflammation, leading to temporary swelling. This swelling should subside on its own. If it persists or worsens, it’s advisable to seek medical attention.
How do you treat nerve damage from blood draw
Nerve damage from a blood draw is rare, but it can happen. If you experience symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or weakness in the area where the blood was drawn, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional. Treatment options for nerve damage may include medications, physical therapy, or, in severe cases, surgery.
How long does it take to recover from a phlebotomy
The recovery time from a phlebotomy, which is the procedure of drawing blood, can vary depending on the individual and the specific circumstances. In general, most people recover quickly and experience minimal discomfort within a day or two. However, complete healing of any bruising or minor complications may take up to two weeks.
What is the most common complication of phlebotomy
The most common complication of phlebotomy is the formation of a hematoma, which is a bruise-like swelling caused by blood leaking into the surrounding tissue. While hematomas are generally harmless and resolve on their own, they can sometimes cause pain and discomfort. If you’re concerned about a hematoma, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider.
What does nerve damage feel like
Nerve damage from a blood draw can cause various sensations, including numbness, tingling, weakness, or a sharp shooting pain. These symptoms may occur at or around the site where the blood was drawn. If you suspect nerve damage, it’s important to seek medical attention to evaluate and treat the condition appropriately.
Can your body repair damaged blood vessels
Yes, the body has a remarkable ability to repair damaged blood vessels. Once a blood vessel is injured, the body initiates a process called hemostasis to stop bleeding and then proceeds with tissue repair. The damaged blood vessel undergoes healing through the formation of a blood clot, the growth of new cells, and the reestablishment of the vessel’s integrity.
What is the most common patient concern when having blood drawn
One of the most common concerns among patients when having blood drawn is the fear of pain. While it’s normal to feel some discomfort during the procedure, most blood draws are relatively quick and cause only minimal pain. The healthcare professional performing the blood draw will do their best to minimize any discomfort you may experience.
Can damaged vessels be reversed
In many cases, damaged blood vessels can be repaired and restored to their normal function. The body’s natural healing processes can often resolve minor vessel injuries. However, severe vessel damage may require medical intervention, such as surgical repair or the placement of stents to restore blood flow in larger vessels.
Can blood vessels heal themselves
Yes, blood vessels have the ability to heal themselves to a certain extent. The body’s healing mechanisms, such as blood clot formation and the growth of new cells, play a vital role in repairing injured vessels. However, it’s important to note that severe or repeated vessel damage may hinder the body’s ability to fully repair them.
How long do blood vessels take to repair
The time it takes for blood vessels to repair can vary depending on the extent of the damage. Minor injuries may heal within a few days or weeks, while more severe damage may require several weeks or months to fully repair. It’s essential to give your body the time it needs to heal and to consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your vessel’s healing progress.
Can veins form scar tissue
Veins can develop scar tissue in response to injury or repeated punctures, such as those that occur during blood draws. The formation of scar tissue can make future blood draws more challenging and may lead to difficulties in locating and accessing veins. If you have a history of scar tissue formation, it’s important to communicate this with the healthcare professional performing the blood draw.
How do I know if I have nerve damage from a blood draw
If you suspect nerve damage from a blood draw, there are symptoms you can look out for. These may include numbness, tingling, weakness, or a burning sensation in the area where the blood was drawn. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical attention for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
How do you know if your vein is blown
A blown vein refers to a vein that has been punctured or damaged, causing it to become non-functional. Signs of a blown vein may include sudden pain, swelling, or bruising at the site of the blood draw. Additionally, a failed attempt to draw blood or insert an IV catheter may indicate a blown vein. If you suspect a blown vein, consult with a healthcare professional for further assessment and alternative options.
Can I sue for nerve damage from a blood draw
Although nerve damage from a blood draw is a rare occurrence, it does happen in some cases. If you believe you have experienced nerve damage due to negligence or malpractice during a blood draw procedure, it may be possible to file a legal claim. Consultation with a medical malpractice attorney is recommended to explore your options and determine the best course of action.
Is it normal for a hematoma to harden
Yes, it is normal for a hematoma, which is a collection of blood under the skin, to harden as it progresses through the stages of healing. Initially, a hematoma may feel soft or spongy, but over time, it can become firm or even slightly lumpy. If you’re concerned about the hardness or appearance of a hematoma, don’t hesitate to consult with your healthcare provider.
What are the side effects of getting blood drawn
While getting blood drawn is generally safe, some individuals may experience side effects. These can include temporary discomfort or pain at the puncture site, bruising, mild dizziness, or, rarely, fainting. If you have concerns about potential side effects or experience unusual symptoms after a blood draw, reach out to your healthcare provider for guidance.
How long does it take a vein to heal after a blood draw
Veins typically heal relatively quickly after a blood draw, usually within a few days or weeks. The body’s natural healing processes work to close the puncture site and restore the vein. However, it’s important to avoid unnecessary strain or injury to the area during the healing process to promote optimal healing.
Why is my blood slow drawing
The speed at which blood is drawn can vary depending on factors such as hydration, blood pressure, and the size and condition of your veins. If your blood is slow to draw, it may be helpful to ensure you are adequately hydrated before the procedure. Additionally, informing the healthcare professional about any factors that may affect your blood flow can help optimize the process.
Can you get blood drawn from the same arm
In most cases, you can have blood drawn from the same arm multiple times. However, it’s important to allow sufficient time for the vein to heal between blood draws to minimize the risk of complications, such as bruising or further damage to the vein. Alternating arms for blood draws is generally recommended to reduce the strain on one particular vein.
Does scar tissue in veins go away
Scar tissue in veins, also known as venous fibrosis, does not typically go away on its own. Once scar tissue forms, it tends to persist. However, with proper care and management, the impact of scar tissue on blood flow and future blood draws can be minimized. Communicating your history of scar tissue to healthcare professionals can help them adapt their techniques accordingly.
Is it normal to have a lump after an IV
Having a lump after an IV is relatively common and not typically a cause for concern. The lump is often a result of irritation to the vein or slight bleeding under the skin. It may take a few days or weeks for the lump to subside. If you experience any concerning symptoms or if the lump persists or worsens, consult with your healthcare provider.
Do blood tests damage your veins
Blood tests generally do not cause long-term or significant damage to your veins. However, repeated blood tests or difficult blood draws with multiple attempts can lead to temporary discomfort, bruising, or, in rare cases, damage to the vein. To minimize potential vein damage, healthcare professionals use appropriate techniques and prioritize patient comfort during blood tests.
Remember, if you have any concerns or questions about the aftermath of a blood draw, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice and address any specific issues you may be experiencing. Stay informed, stay curious, and remember that a little humor goes a long way when it comes to making medical matters more approachable.